Monosaccharides
These are the simplest form or sugars,they contain a single chain or carbon atoms with hydroxyl groups attached to each carbon. Monosaccharides can be formed with 3 carbons (triose), 5 (pentose), and 6 (hexose). Depending on the location of the carboxyl group, these are also categorized into aldehyde or ketone.
Ribose - a component of RNA
Ribulose - used in photosynthesis
Glucose - a source of energy for all cells
Galactose - a component of lactose, milk sugar
Fructose - fruit sugar
Simple sugars with 5 or more carbon atoms forms a ring-shaped structure when dissolved in water, the location of the hydroxyl group is therefore at random. Take glucose for example, if the hydroxyl group of carbon 1 ends up above the horizontal plane, it is said to be beta-glucose. If the hydroxyl group is below the horizontal plane, the molecule is said to be alpha-glucose.
Oligosaccharides
These are sugars containing two or three monosaccharides attached to each other by covalent bonds called glycosidic linkages.
The most important oligosaccharides are maltose, sucrose, and lactose.
Maltose - made by 2 alpha-glucose attached by a 1-4 glycosidic linkage. It is a disaccharide found in grains that is used in the production of beer.
Sucrose - made from an alpha-glucose and an alpha-fructose attached by a 1-2 glycosidic linkage. Sucrose is the most common table sugar. It is used by plants to transport glucose and other simple sugars, and they are found in high concentrations in sugar cane, sugar beets, and sugar maple trees.
Lactose - a type of sugar found in milk, made by a glucose attached by a galactose.
Polysaccharides
These are complex carbohydrates (polymers composed of hundreds to thousands of monosaccharide monomers held together by glycosidic linkages). They serve as energy storage, and structural support in most organisms.
1. Starch
This is the most significant type of energy storage in plants, they come in two different types amylose and amylopectin.
Amylose is a straight chain polymer of alpha-glucose with alpha 1-4 glycocidic linkage.
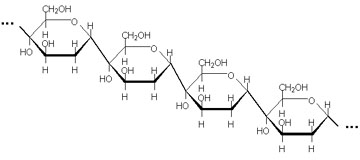 a
aAmylopectin are branched glucose chains with alpha 1-4 linkages and alpha 1-6 linkages. The branching makes amylopctin coils and insoluble in water.

2. Glycogen
Humans store energy in the form of glycogen. Structure wise, glycogen is much like amylopectin but with much more branches. Small amounts of glycogen are found in human muscle and liver cells.
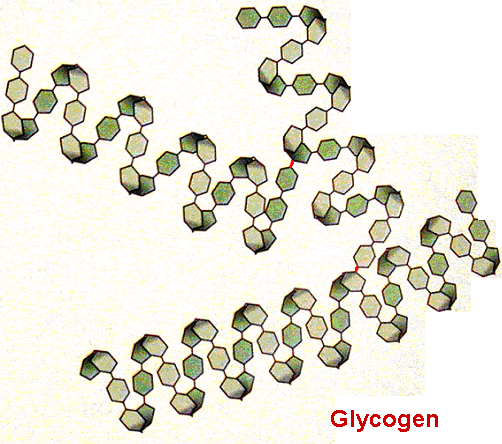
3. Cellulose
This is the major structural polysaccharide in plants, and a major component of cell walls. Unlike amylose, cellulose are a straight chain of beta-glucose held together by beta 1-4 glycosidic linkages. Adjacent cellulose chains are held together by hydrogen bonds, given them a strong structure.

4. Chitin
This is the hard exoskeleton of insects and other animals such as crabs and lobsters, and other cell walls of many fungi. The monomer is a glucose to which a nitrogen-containing group is attached to the carbon 2 position.



No comments:
Post a Comment